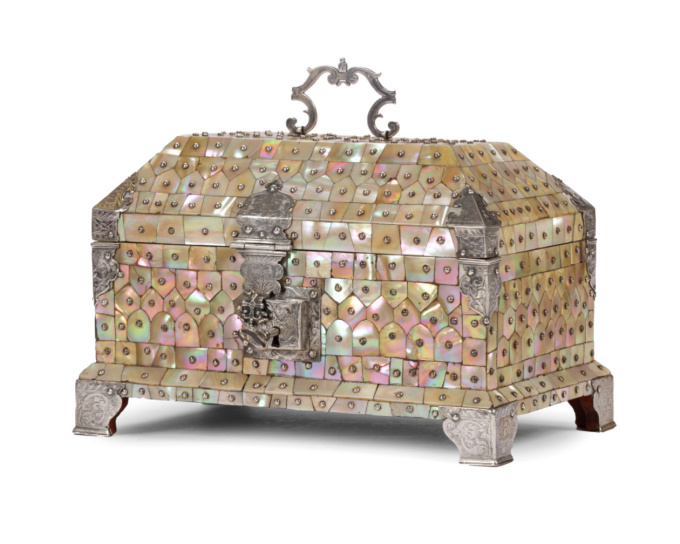
An exceptional Indo-Portuguese colonial mother-of-pearl veneered casket with silver mounts 1650 - 1700
Onbekende Kunstenaar
HoutParelParelmoerZilver
16 ⨯ 24 ⨯ 16 cm
Prijs op aanvraag
Zebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
- Over kunstwerkAn exceptional Indo-Portuguese colonial mother-of-pearl veneered casket with silver mounts
India, Gujarat, 2nd half of the 16th century, the silver mounts Goa or probably Lisbon
H. 16 x W. 24.6 x D. 16.1 cm
An exceptional Gujarati casket with a rectangular box and truncated pyramidal lid (with slopes on each side and a flat top) made from exotic wood, probably teak (Tectona grandis), covered with a mother-of-pearl mosaic. The tesserae, cut from the shell of the green turban sea snail (Turbo marmoratus, a marine gastropod) in the shape of fish scales, are pinned to the wooden structure with silver ball-headed nails. The casket is set on bracket feet on the corners. The masterfully engraved decoration of the silver mounts follows the most refined and erudite Mannerist repertoire of rinceaux and ferroneries dating from the mid-16th century. The high quality and refinement of the silver mounts and, likewise, the silver nails that replaced the original brass pins used to hold the mother-of-pearl tesserae in place indicate the work of a silversmith probably working in Lisbon in the second half of the 16th century. The Indian origin of this production, namely from Cambay (Khambhat) and Surat in the present state of Gujarat in north India, is, as for the last three decades, consensual and fully demonstrated, not only by documentary and literary evidence - such as descriptions, travelogues and contemporary archival documentation - but also by the survival in situ of 16th-century wooden structures covered in mother-of-pearl tesserae. A fine example is a canopy decorating the tomb (dargah) of the Sufi saint, Sheik Salim Chisti (1478-1572) in Fatehpur Sikri in Agra district in the state of Uttar Pradesh, north India. This is an artistic production, geometric in character and Islamic in nature, where usually the mother-of-pearl tesserae form complex designs of fish scales or, similar to the dishes also made using the same technique, with the thin brass sheets and pins, stylized lotus flowers. The truncated pyramidal shape corresponds, like their contemporary tortoiseshell counterparts also made in Gujarat, to a piece of furniture used in the Indian subcontinent within the Islamic world prior to the arrival of the first Portuguese. This shape, in fact, is very old and peculiar to East-Asian caskets, chests or boxes used to contain and protect Buddhist texts, the sutras. EnquireA similar chest is the famous and large reliquary chest from Lisbon cathedral that once contained the relics of the city's patron saint, Saint Vincent. Both match in shape, having the same kind of socle or pedestal and bracket feet, and in their engraved silver mountings, featuring the same type of refined, erudite decoration. Their differences lie in the silver borders that frame the entire length of the edges of the chest (both the box and the lid), pinned with silver nails, and on the lock plate, shaped like a coat of arms in the Lisbon example. Given the exceptional dimensions of the reliquary casket from Lisbon cathedral (48 x 65 x 42 cm), the goldsmith responsible for its mounting opted to place two bracket-shaped side handles instead of a top handle, as in our casket. Another similar example, probably mounted in the same Lisbon workshop as the other examples from this small group, belongs to the Seville Cathedral and remains almost unknown. It shares many features in common with the one in the Lisbon cathedral, namely the use of engraved silver borders running along the edges, protecting the casket. An aspect that distinguished it from the others is the use of tesserae cut from Turbo marmoratus, which show a higher iridescence but also cut from the shell of the pearl oyster, probably Pinctada radiata or Pinctada maxima, given the whitish hue of the base colour. Nevertheless, the type of square-like lock plate is similar to our casket.
Another example, slightly larger but with less silver mounts, is in the collection of the Kunstkammer Wien in the Kunsthistorischen Museums in Vienna (inv.no. GS Kap 5) and belonged to the Habsburger Family. The same type of large silver ball-headed nails seems to be characteristic of this small, rare and important group, of which the present example is the second known example in private hands, given that the others have been in their current place since the time they entered their collections in the late 16th century or the first years of the 17th century. - Over kunstenaar
Het kan voorkomen dat een kunstenaar of maker onbekend is.
Voor sommige werken is het niet te bepalen door wie het gemaakt is of dat het is gemaakt door (een groep) ambachtslieden. Voorbeelden zijn beelden uit de Oudheid, meubels, spiegels of handtekeningen die vaak niet duidelijk of leesbaar zijn. Maar ook sommige werken zijn helemaal niet gesigneerd.
Ook kunt u de volgende beschrijving vinden:
•"Toegeschreven aan …." waarschijnlijk een werk van de kunstenaar maar niet zeker of gedeeltelijk
•“Atelier van ….” of werkplaats van” een werk uitgevoerd in het atelier of atelier van de kunstenaar, eventueel onder zijn toezicht
•“Cirkel van ….” een werk uit de periode van de kunstenaar die zijn invloed laat zien, nauw verbonden met de kunstenaar maar niet noodzakelijkerwijs zijn leerling
•“Stijl van ….” of “Volger van ….” een werk uitgevoerd in de stijl van de kunstenaar, maar niet noodzakelijk door een leerling; kan eigentijds of bijna eigentijds zijn
•“Wijze van ….” een werk in de stijl van de kunstenaar maar van latere datum
•"Na …." een kopie (van welke datum dan ook) van een werk van de kunstenaar
•“Getekend…”, “Gedateerd….” of “Ingeschreven” dan is het werk gesigneerd/ gedateerd/ ingeschreven door de kunstenaar. De toevoeging van een vraagteken duidt op een element van twijfel
•"Met handtekening ...", "Met datum ...", "Met opschrift..." of “Draagt signatuur/datum/opschrift” dan is de handtekening/datum/opschrift toegevoegd door iemand anders dan de kunstenaar
Bent u geïnteresseerd om dit kunstwerk te kopen?
Related artworks
Onbekende Kunstenaar
Twee studieportretten van Mas Marco Kartodikromo1900 - 1950
Prijs op aanvraagZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
Onbekende Kunstenaar
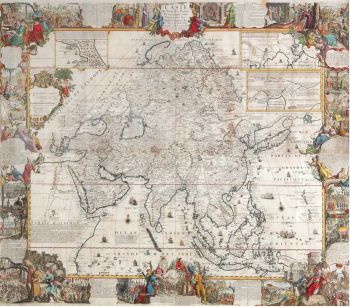
A large wall map of Asia by Nicolas de Fer 1647 - 1720
Prijs op aanvraagZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
1 - 4 / 12Onbekende Kunstenaar
An Indian part-gilt silver-clad ceremonial sceptre or mace with a tiger’s head1850 - 1900
Prijs op aanvraagZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
 Gecureerd door
Gecureerd doorDanny Bree
Onbekende Kunstenaar
Silver Russian Presentation Easter Egg1880 - 1899
Prijs op aanvraagH.W.C. Dullaert Art & Antiques Dealer
1 - 4 / 24Onbekende Kunstenaar
Japanese transition-style lacquer coffer 1640 - 1650
Prijs op aanvraagZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
Onbekende Kunstenaar
A Dutch colonial Indonesian betel box with gold mounts1750 - 1800
Prijs op aanvraagZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
Onbekende Kunstenaar
A Surinam-themed Amsterdam long-case clock1746 - 1756
Prijs op aanvraagZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
 Gecureerd door
Gecureerd doorGallerease Magazine
Onbekende Kunstenaar
A Surinam-themed Amsterdam long-case clock1746 - 1756
Prijs op aanvraagZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
 Gecureerd door
Gecureerd doorGallerease Magazine
Willem Witsen
Vintage portretfoto van Paul Verlaine (zittend)1850 - 1900
Prijs op aanvraagKunsthandel Pygmalion
1 - 4 / 24- 1 - 4 / 24
Onbekende Kunstenaar
A large wall map of Asia by Nicolas de Fer 1647 - 1720
Prijs op aanvraagZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
Onbekende Kunstenaar
Dutchmen in miniature (Netsuke)1700 - 1900
Prijs op aanvraagZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
Onbekende Kunstenaar
Twee studieportretten van Mas Marco Kartodikromo1900 - 1950
Prijs op aanvraagZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
1 - 4 / 12